The American Statistical Association released an important statement and supporting paper concerning the use and interpretation of statistical significance and p-values in statistical research.
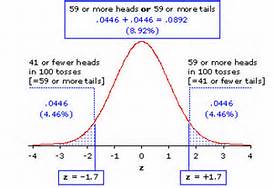
The American Statistical Associations’ statement notes that the increased quantification of scientific research and a proliferation of large, complex data sets, often referred to as Big Data, has expanded the scope for statistics. Accordingly, the importance of appropriately chosen techniques, properly conducted analyses, and correct interpretation has also increased.
This statement by the ASA furthers, and in some ways solidifies, the ground roots “counter-statistical significance” movement that many economists and statisticians, such as Steve Zillack and Diedre McCloskey, have been working on for decades.
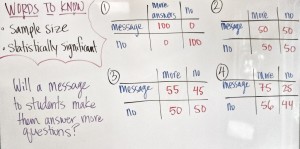
According to the ASA statement “The p-value [and the concept of statistical significance] was never intended to be a substitute for scientific reasoning,” said Ron Wasserstein, the ASA’s executive director. In research analysts use the data to calculate a p-value which shows how consistent the data is with the research hypothesis. A small p-value is typically interpreted as having a small likelihood of being consistent with the research hypothesis. In research papers, small p-values are in essence viewed as a ‘good thing’ and according to the ASA statement, are more favored by journal editors for publication.
The ASA statement argues against this approach. Instead, the ASA statement states that “Well-reasoned statistical arguments contain much more than the value of a single number and whether that number exceeds an arbitrary threshold.”
See:
Ronald L. Wasserstein & Nicole A. Lazar (2016): The ASA’s statement on p-values: context, process, and purpose, The American Statistician, DOI: 10.1080/00031305.2016.1154108
Ziliak, S.T., and McCloskey, D.N. (2008), The Cult of Statistical Significance: How the Standard Error Costs Us Jobs, Justice, and Lives, Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press
Ziliak, S.T. (2010), “The Validus Medicus and a New Gold Standard,” The Lancet, 376, 9738, 324-325.


 Here at Employstats, our analysts utilize the statistical software package Stata for data management, as well as data analysis in all types of wage & hour, economic, and employment analyses. With Stata, all analyses can be reproduced and documented for publication and review.
Here at Employstats, our analysts utilize the statistical software package Stata for data management, as well as data analysis in all types of wage & hour, economic, and employment analyses. With Stata, all analyses can be reproduced and documented for publication and review.